The Ultimate Garment Manufacturing Glossary

Estimated Reading Time: ~3 minutes
Introduction
The complete process of garment manufacturing depends on specific technical terms and traditional artisanal skills. Fashion designers factory managers and fabric buyers who learn these essential terms will enhance their communication and improve quality control and production efficiency.
1. Cutting & Patternmaking
- Cutting: The first step of turning pattern pieces into fabric cutouts for sewing preparation.
- Drafting: The process of making paper patterns from design sketches for establishing measurements and proportions.
- Prototype: A preliminary sample garment based on the pattern, used to test fit and design.
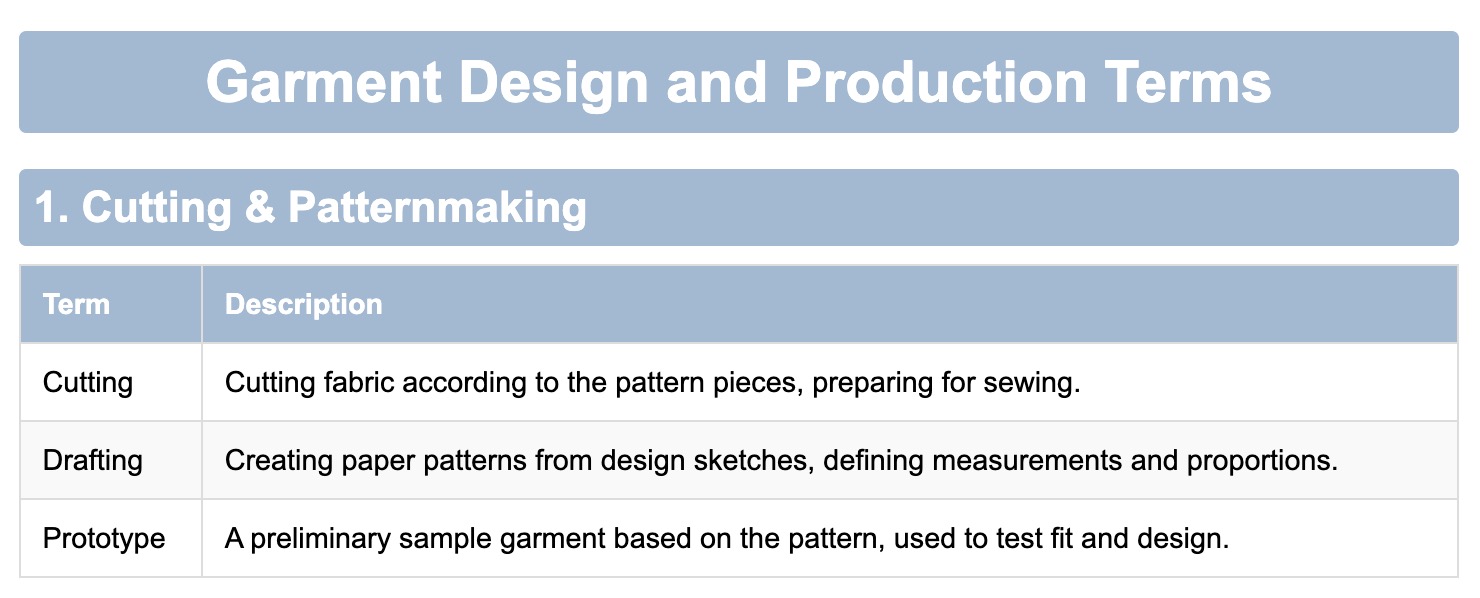
2. Sewing Techniques
- Sewing: Fabric joining occurs by machine or hand to build the garment.
- Seam Allowance: The area where fabric edges meet before stitching preserves exact dimensions of the finished garment.
- Seam: The stitched joint in a garment, critical for strength and appearance.
- Overlocking: Using a serger to finish raw edges and prevent fraying.
- Flat Seam: A flat, even seam often used on internal joins for comfort.
- Double Stitch: Two parallel stitches for extra durability and decorative effect.
- Binding: Encasing seam allowances with a narrow fabric strip for a neat finish.
- Topstitching: Decorative stitching on the garment surface that also secures seam allowances.
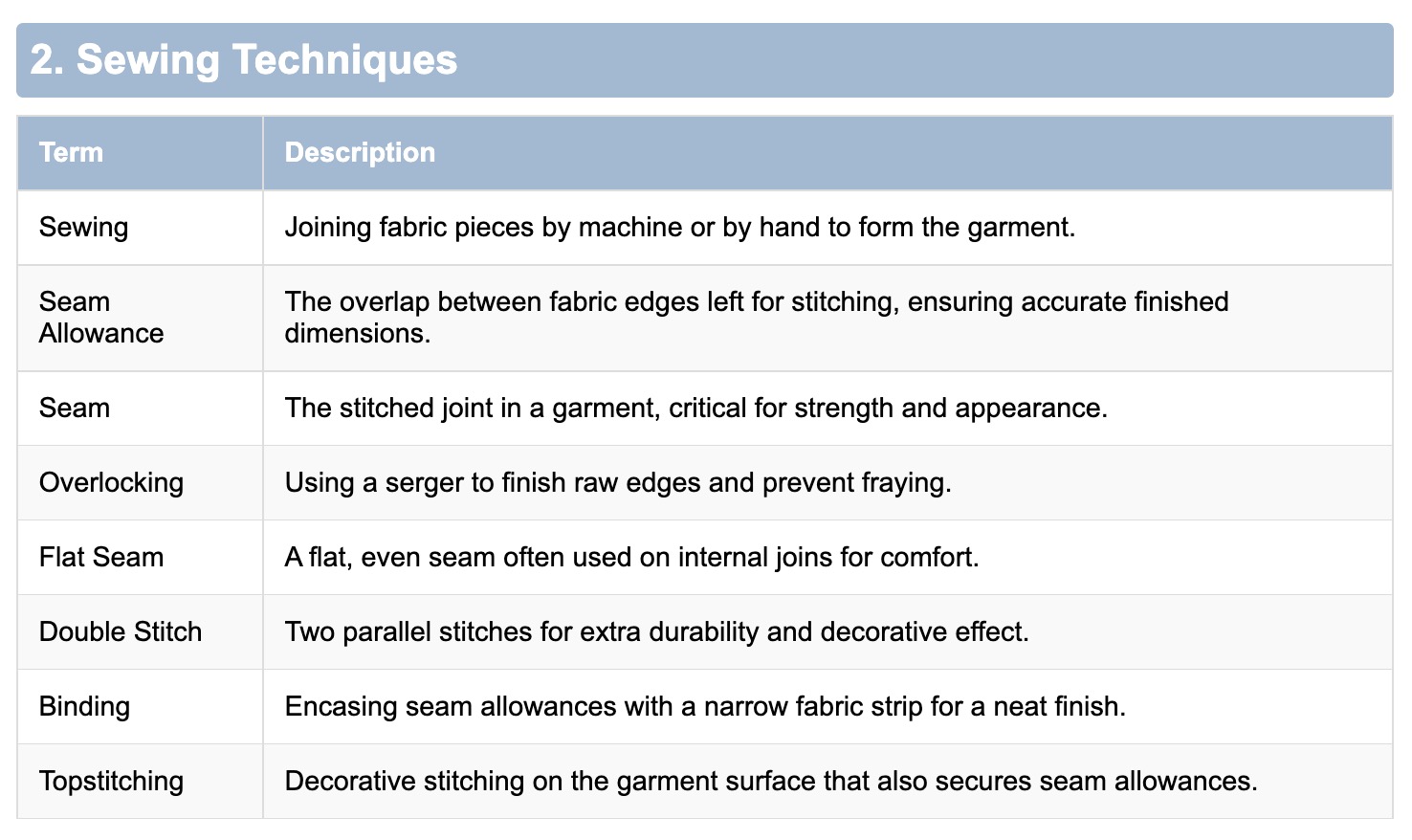
3. Details & Embellishments
- Zipper: A common closure element for garments and pockets.
- Button: Fastening element secured through a buttonhole, available in myriad styles.
- Buttonhole: The stitched opening for button insertion, machine- or hand-sewn.
- Dart: Folds sewn into fabric to shape the garment’s silhouette.
- Ruffle / Flounce: Decorative wavy edges that add romantic flair.
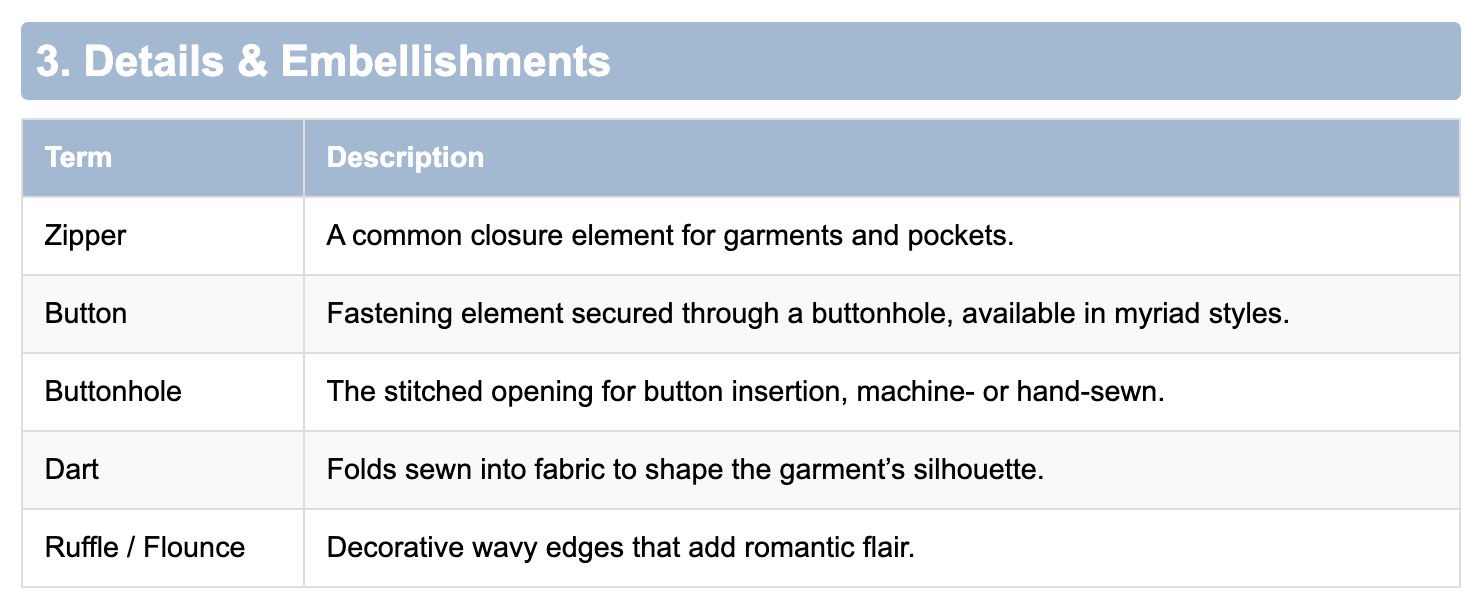
4. Structure & Silhouette
- Collar: The design and shape of the garment’s neckline (e.g., spread, stand).
- Sleeve: The style of the arm covering (e.g., raglan, puff).
- Waistline: The position and cut at the garment’s waist area.
- Hem: The finished bottom edge of a garment, folded or stitched.
- Lining: Inner fabric layer for comfort and improved drape.
- Shoulder Pad: Padding inserted at the shoulders to create structure.
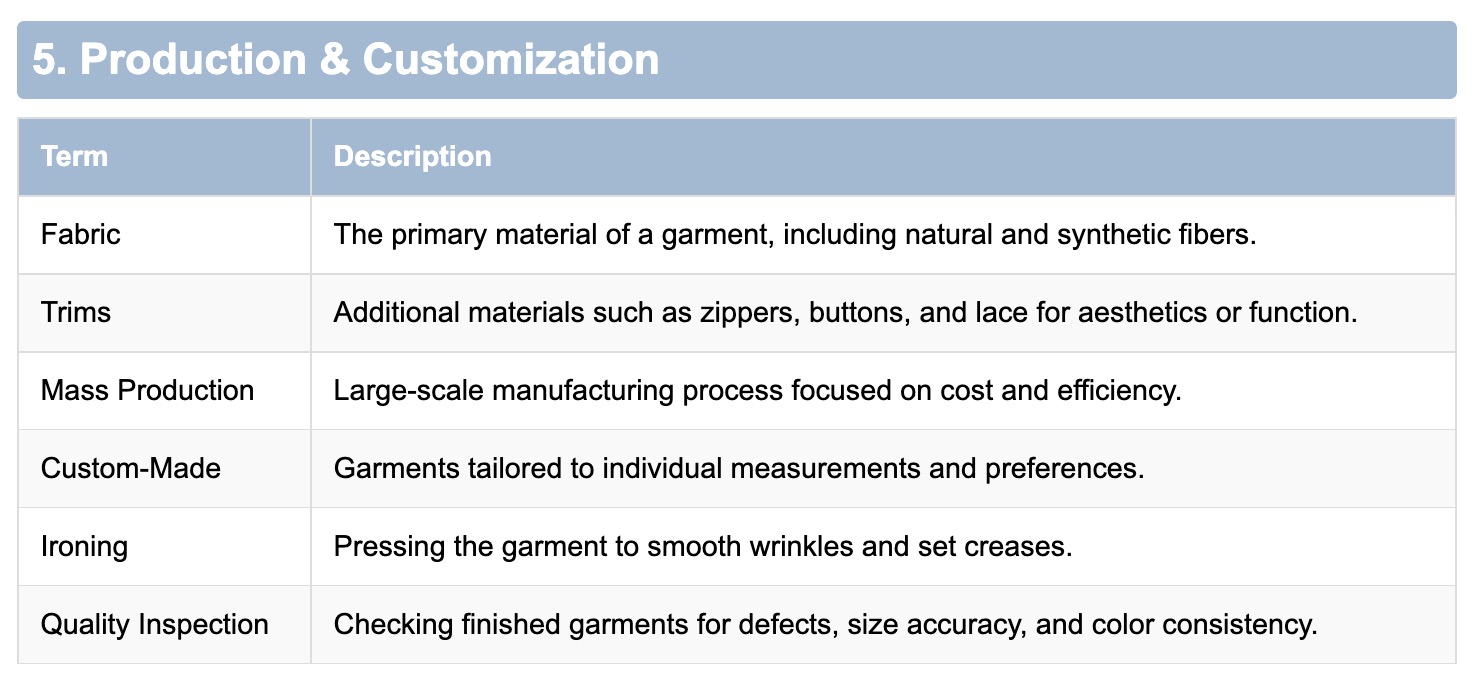
5. Production & Customization
- Fabric: The primary material of a garment, including natural and synthetic fibers.
- Trims: Additional materials such as zippers, buttons, and lace for aesthetics or function.
- Mass Production: Large-scale manufacturing process focused on cost and efficiency.
- Custom-Made: Garments tailored to individual measurements and preferences.
- Ironing: Pressing the garment to smooth wrinkles and set creases.
- Quality Inspection: Checking finished garments for defects, size accuracy, and color consistency.
Customization Services by LYDENIM
🎨 Want custom denim fabrics or unique custom denim garment? LYDENIM specializes in tailor-made solutions to meet your design and production needs.
🛍️ Explore & Get Inspired: Browse our fabric selections and discover design ideas on LYDenim.
🌐 Elastic Clothing: Check out our offerings on MyAlibaba. 📩 Contact Us: Reach out at malone@lydenim.com.
Create your denim masterpiece with LYDENIM—your trusted partner for stretch fabric and custom denim solutions.
