L'histoire du coton - Caractéristiques du coton
Temps de lecture estimé : ~5 minutes
Introduction
Cotton, a natural fiber, is a cornerstone of textiles due to its softness, breathability, and versatility. From everyday apparel to luxury bedding, cotton meets diverse needs. This article explores cotton classifications based on purity, origin, processing, fiber characteristics, and manufacturing processes, providing a detailed guide to help readers make informed choices for clothing and home textiles.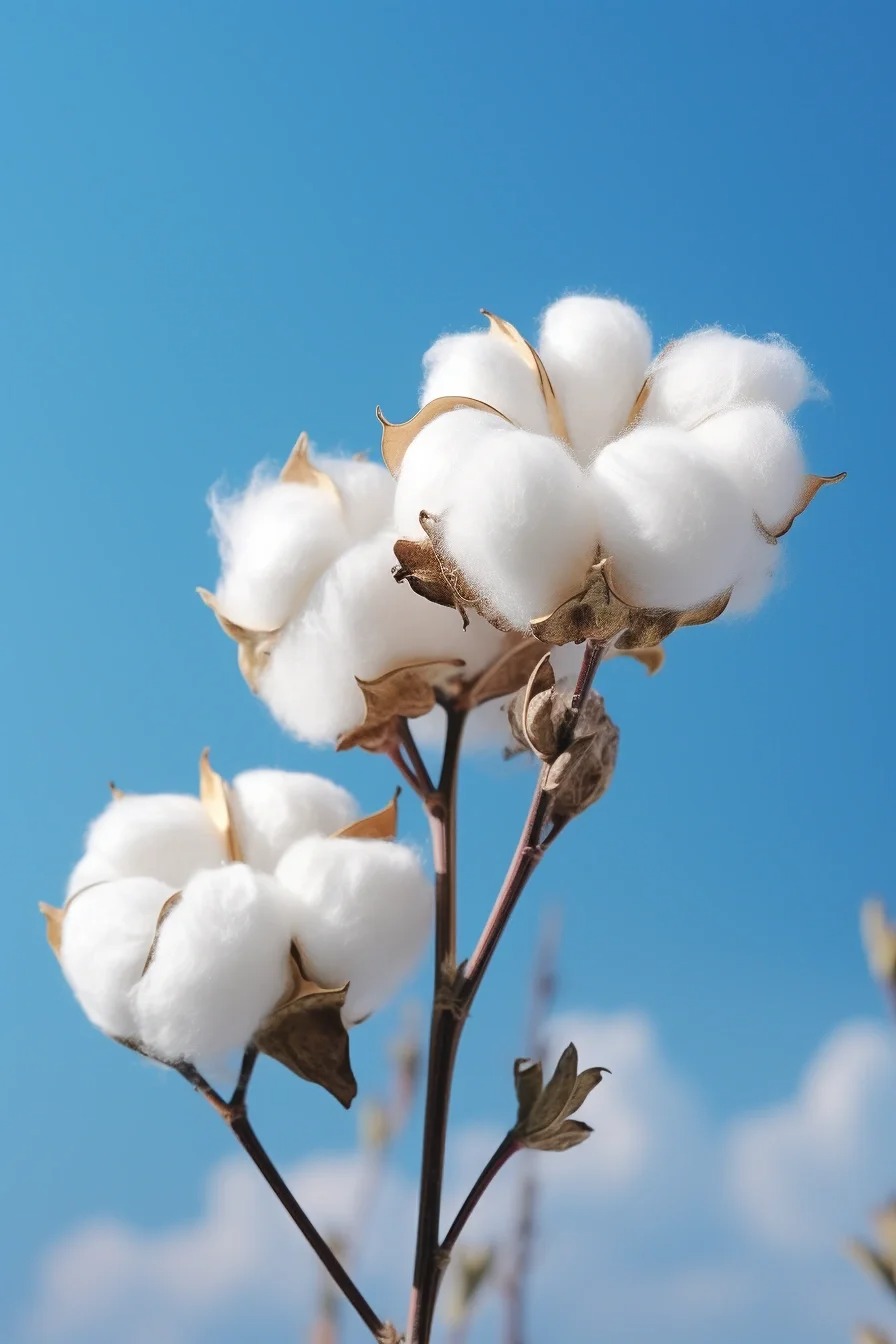
Classification by Purity
The purity of cotton determines whether it is composed entirely of cotton fibers or blended with other materials.
| Taper | Définition | Caractéristiques | Utilisations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pure Cotton (100% Cotton) | Fabric made entirely of cotton fibers | Breathable, absorbent, soft, hypoallergenic | T-shirts, underwear, sheets, towels |
| Blended Cotton | Cotton mixed with fibers like spandex or polyester | Adds stretch, durability, or warmth | Sportswear, shirts, pants |
- Pure Coton (100% Cotton)
Pure cotton is renowned for its breathability, moisture absorption, and comfort, ideal for warm weather and sensitive skin. It is commonly used in T-shirts, underwear, sheets, and towels. Note that “pure cotton” or “all cotton” should indicate 100% cotton, not blends like 10% cotton with 90% polyester. Always check labels for exact composition.
- Blended Cotton
Blended cotton combines cotton with other fibers to enhance functionality:- Cotton-Spandex (Lycra): Typically 95% cotton and 5% spandex, offering stretch and recovery for sportswear and fitted jeans.
- Cotton-Polyester: Common ratios like 60/40 or 50/50 provide wrinkle resistance and easy care, used in shirts and pants.
- Other Blends: Cotton-wool (warmth, for sweaters), cotton-silk (luxury, for blouses), cotton-linen (breathability, for summer wear).

Classification by Origin
Cotton from different regions varies in quality due to climate and soil conditions.
| Taper | Origine | Caractéristiques | Utilisations |
|---|---|---|---|
| U.S. Cotton (Upland Cotton) | U.S., Central America, Caribbean | Medium-length fibers, versatile | Everyday apparel, home textiles |
| U.S. Cotton (Pima Cotton) | Southwestern U.S. | Long-staple, soft, durable | Luxury shirts, sheets, towels |
| Xinjiang Cotton | Xinjiang, China | Long fibers, soft, high quality | Premium bedding, apparel |
| Egyptian Cotton | Egypt (and other long-staple regions) | Extra-long fibers, soft, durable, lustrous | Luxury sheets, towels, shirts |
| Australian Cotton | Australie | High quality, sustainable, uniform fibers | Premium textiles, apparel |
| Brazilian Cotton | Brazil | Rain-fed, high quality, eco-friendly | Various textiles, apparel |
| African Cotton | Africa (e.g., Benin, Burkina Faso) | Hand-picked, eco-friendly, variable quality | General textiles, apparel |
- U.S. Cotton (Upland Cotton)
Accounting for 90% of global cotton production, Upland cotton is versatile and durable, used in T-shirts, jeans, and home textiles due to its medium-length fibers. - U.S. Cotton (Pima Cotton)
A long-staple cotton from the southwestern U.S., Pima is soft, durable, and luxurious, ideal for high-end shirts, bedding, and towels. - Xinjiang Cotton
Grown in China’s Xinjiang region, this cotton is prized for its long fibers and softness, perfect for premium textiles. Ethical concerns regarding labor practices may influence consumer choices, so consider sustainable sourcing. - Egyptian Cotton
Known for its extra-long staple fibers (over 1 inch), Egyptian cotton is soft, durable, and lustrous, a top choice for luxury bedding, towels, and shirts. Similar long-staple cottons, like Pima, may also be labeled as Egyptian. - Australian Cotton
Australian cotton is high quality and sustainable, with uniform, strong fibers. Produced with advanced technology to reduce pesticide use, it is exported to Southeast Asia for premium yarn and textiles. - Brazilian Cotton
With 92% rain-fed cultivation, Brazilian cotton is eco-friendly and high quality, tested with High Volume Instrument (HVI) for consistency. It is used in various textiles and exported to Vietnam and Indonesia. - African Cotton
A major global cotton producer, Africa (e.g., Benin, Burkina Faso) uses hand-picking to minimize chemical pollution, though quality may vary due to contaminants. Mali’s Bazin and mud cloth are culturally significant. African cotton suits general textiles.
Classification by Processing
Processing techniques enhance cotton’s texture and performance.
| Taper | Processus | Caractéristiques | Utilisations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Combed Cotton | Combed to remove short fibers and impurities | Smooth, durable, less pilling | High-end shirts, baby clothing |
| Washed Cotton | Pre-washed to remove dyes and pre-shrink | Reduced shrinkage, soft, “worn-in” feel | Denim jeans, casual wear |
- Combed Cotton
Combed cotton removes short fibers and impurities, resulting in smoother, stronger yarn with less pilling. It is used in high-end shirts and baby clothing for its refined texture. - Washed Cotton
Pre-washed to remove excess dyes and pre-shrink, washed cotton offers a softer, “lived-in” feel with minimal shrinkage, popular in denim jeans and casual apparel.
Classification by Fiber Characteristics
Fiber length and coarseness impact the fabric’s texture and durability.
| Taper | Définition | Caractéristiques | Utilisations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Long-Staple Cotton | Fibers longer than 1 inch (2.5 cm) | Strong, smooth, less pilling | Luxury bedding, shirts, towels |
| Fine Cotton | Fine, high-quality fibers | Soft, smooth, similar to long-staple | Premium textiles |
| Coarse Cotton | Short, coarse fibers | Durable, textured | Denim, canvas, workwear |
- Long-Staple Cotton
With fibers exceeding 1 inch, long-staple cotton (e.g., Egyptian, Pima) produces strong, smooth fabrics that resist pilling, ideal for luxury bedding and shirts. - Fine Cotton
Fine cotton refers to high-quality, fine-fibered cotton, often overlapping with long-staple cotton, used in premium textiles. - Coarse Cotton
Short-fibered and textured, coarse cotton is durable and suited for rugged fabrics like denim, canvas, and workwear.
Classification by Manufacturing Process
The manufacturing process determines the fabric’s appearance and functionality.
| Taper | Processus | Caractéristiques | Utilisations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Knitted Cotton | Interlocked yarn loops | Stretchy, comfortable, body-conforming | T-shirts, sweaters, socks |
| Pique Cotton | Knit with raised honeycomb texture | Breathable, textured | Polo shirts, golf shirts |
| Sateen Cotton | Woven with smooth, silky finish | Soft, lustrous | Bedding, upholstery |
- Knitted Cotton
Formed by interlocking yarn loops, knitted cotton is stretchy and comfortable, ideal for T-shirts, sweaters, and underwear. - Pique Cotton
A knitted cotton with a raised, honeycomb-like texture, pique cotton is breathable and used in polo and golf shirts. - Sateen Cotton
Woven to create a smooth, silky surface, sateen cotton is soft and lustrous, commonly used in bedding and upholstery.
How to Choose the Right Cotton Type?
Selecting the appropriate cotton depends on several factors:
- But: Pure cotton for comfort, blended cotton for functionality like stretch or durability.
- Confort: Combed or long-staple cotton for softness, washed cotton for a pre-worn feel.
- Budget: Egyptian and Xinjiang cotton are premium, while coarse cotton and blends are more affordable.
- Durabilité: Opt for organic or sustainably sourced cotton (e.g., Australian, Brazilian) to reduce environmental impact.
Conclusion
Cotton’s versatility stems from its diverse forms and treatments. From the comfort of pure cotton to the functionality of blends, from the versatility of U.S. cotton to the luxury of Egyptian cotton, each type offers unique benefits. Understanding these classifications empowers consumers to select the ideal cotton for their clothing or home textiles, balancing comfort, quality, and sustainability.
Services de personnalisation
For personalized cotton clothing tailored to your preferences and body shape, Explore our fabrics at lydenim.com or find design inspiration on Alibaba. For more details, email malone@lydenim.com.
